
Neural Tube Defects Develop During The First Month. Neural tube defects (NTDs) are extremely dangerous birth defects that affect the central nervous, which includes the spine and brain. Neural tube birth defects generally develop during the first month of conception. The neural tube is an early embryonic structure, which develops 18 to 30 days after […]
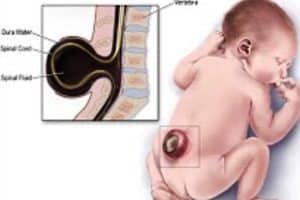
Neural Tube Defects Develop During The First Month. Neural tube defects (NTDs) are extremely dangerous birth defects that affect the central nervous, which includes the spine and brain. Neural tube birth defects generally develop during the first month of conception. The neural tube is an early embryonic structure, which develops 18 to 30 days after conceptions. Beginning as a flat plate of tissues, the neural tube then forms two ridges of tissue that fold up and fuse, forming cylinder or tube. The neural tube forms the brain and spinal cord.
Neural tube defects happen when the tube fails to close fully. Neural tube defects occur in approximately 1 in every 1,000 to 2,000 live births in the United States, or in about 1,500 to 2,000 babies each year. Children who have a Neural tube defect, an estimated 95% are born to couples with no family history of these defects.
Neural tube defects may be detected with prenatal tests, such as ultrasound and amniocentesis. Past research has discovered that approximately 50%or more of neural tube defects can be prevented if women consume a folic acid-containing supplement before and during the early weeks of pregnancy in addition to the folate in their diet. The US Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and American Academy of Pediatrics advise that all women of childbearing age who are capable of becoming pregnant should consume 0.4 mg of folic acid daily. Even though the risk for neural tube defects is not entirely reduced by folic acid use.
If you or a loved one has taken prescription drugs while pregnant and given birth to a child who has been diagnosed with a neural tube defect, please fill out the form to the right for a free case evaluation by a qualified birth defect attorney or call us at 1-800-YOURLAWYER (1-800-968-7529).


